7 GeoSpatial Datasets for Computer Vision Projects

Whether you’re focused on autonomous vehicles, smart city planning, or environmental monitoring, geospatial datasets offer the depth and detail you need to achieve superior results.
But finding high-quality, geospatially accurate datasets for computer vision projects is not a piece of cake.
Many businesses struggle with data that lacks the necessary context or precision, leading to less effective models and solutions.
A survey by Datanami reveals that 33%-38% of respondents reported failures or delays in AI projects due to poor data quality.
Without the right datasets, your computer vision models may miss out on critical geographic details, resulting in inaccuracies and inefficiencies.
This can mean wasted resources, slower development times, and ultimately, less impactful solutions.
Wondering what are the right geospatial datasets that can bridge the gap and provide the precision and context you need to drive your projects forward.
In this post, we’ll introduce you to seven essential geospatial datasets that can transform how you approach and execute your computer vision initiatives.
What are Geospatial datasets?
Geospatial datasets are sets of data that are linked to specific geographic spaces on the Earth's surface.
These datasets include:
- Terrain,
- Land cover,
- Buildings,
- Roads,
- Rivers,
- And other physical environment variables and characteristics.
Besides, maps, satellite images, aerial pictures, and other spatial formats are frequently used to depict geospatial data.
How do you create geospatial databases?
Geospatial databases can be created using a variety of sources, including satellite imagery, aerial surveys, GPS (Global Positioning System) data, remote sensing technologies, and crowd-sourced contributions.
Databases can include various types of information related to specific geographic areas, such as coordinates (latitude and longitude), elevation, land cover classifications, demographic data, and other relevant details.
How Geospatial data are used?
These datasets are useful for understanding and analyzing geographical patterns. It helps businesses make informed decisions, and build applications in areas like urban planning, environmental monitoring, transportation, agriculture, and disaster management.
Geospatial datasets are increasingly being utilized in computer vision projects to train algorithms to comprehend and analyze images within a geographical context as computer vision and machine learning techniques develop.
Overall, geospatial datasets are critical resources for applications requiring location-based information, such as geospatial analysis, mapping, visualization, and computer vision.
They are critical for comprehending the Earth's surface and making educated decisions in various disciplines.
Also Read: Best Practices For Image Labeling To Improve ML Accuracy
Significance of GeoSpatial Datasets for Computer Vision Projects
Computer vision projects can greatly benefit from the rich data provided by spatial datasets. Here are a few key reasons why:
1. Access to Geographic Context
For computer vision projects, geospatial datasets offer a spatial context. The information can aid in understanding the relationships between various characteristics in an image or a video.
For instance, satellite imaging can reveal details about the geography of a region, the use of land, and the locations of objects on the ground.
2. Large-Scale Datasets
Large-scale geographic datasets frequently provide information on changes throughout time.
Applications like tracking urban development, monitoring environmental change, or understanding transportation patterns can all benefit from this.
3. Precision
Geospatial datasets can also offer exact information about an object's location, which is particularly helpful for applications like autonomous vehicles where precise location data is essential.
4. Integration
Geospatial datasets can be combined with other data sources, such as meteorological or demographic data, to offer a thorough picture of the environment.
The usage of geographic datasets can improve the precision, effectiveness, and utility of computer vision projects, especially those pertaining to large-scale and spatially-oriented applications.
Top 7 GeoSpatial Datasets for Computer Vision Projects
Here are top 7 geospatial datasets that can help you in your computer vision projects are shown below:
1. OpenStreetMap
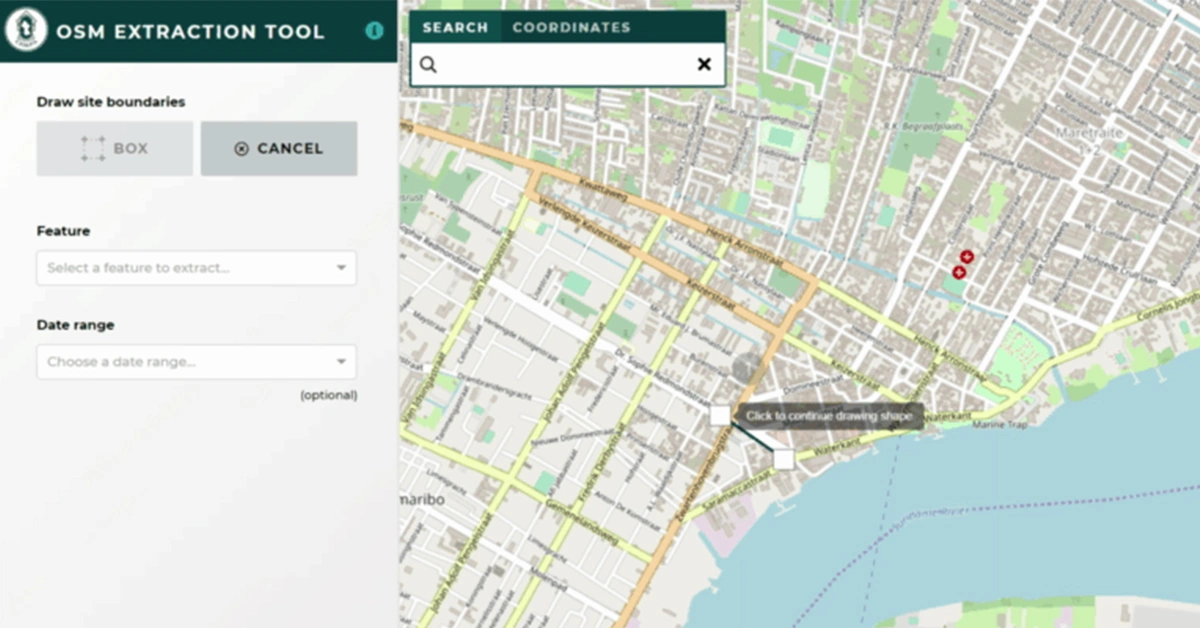
A collaborative initiative called OpenStreetMap (OSM) gives anyone who wants to utilize its access to free geospatial data, including maps.
The dataset is accessible in XML, JSON, and GeoJSON, among other formats. Various computer vision tasks, including object identification, image segmentation, and classification, can be accomplished with OSM.
2. SpaceNet
SpaceNet is a dataset that provides high-resolution satellite imagery and labeled building footprints for machine learning research.
The dataset covers areas of interest in multiple cities around the world, and it includes both RGB and multispectral imagery.
SpaceNet can be used for a variety of computer vision projects, such as object detection, semantic segmentation, and change detection.
3. COCO
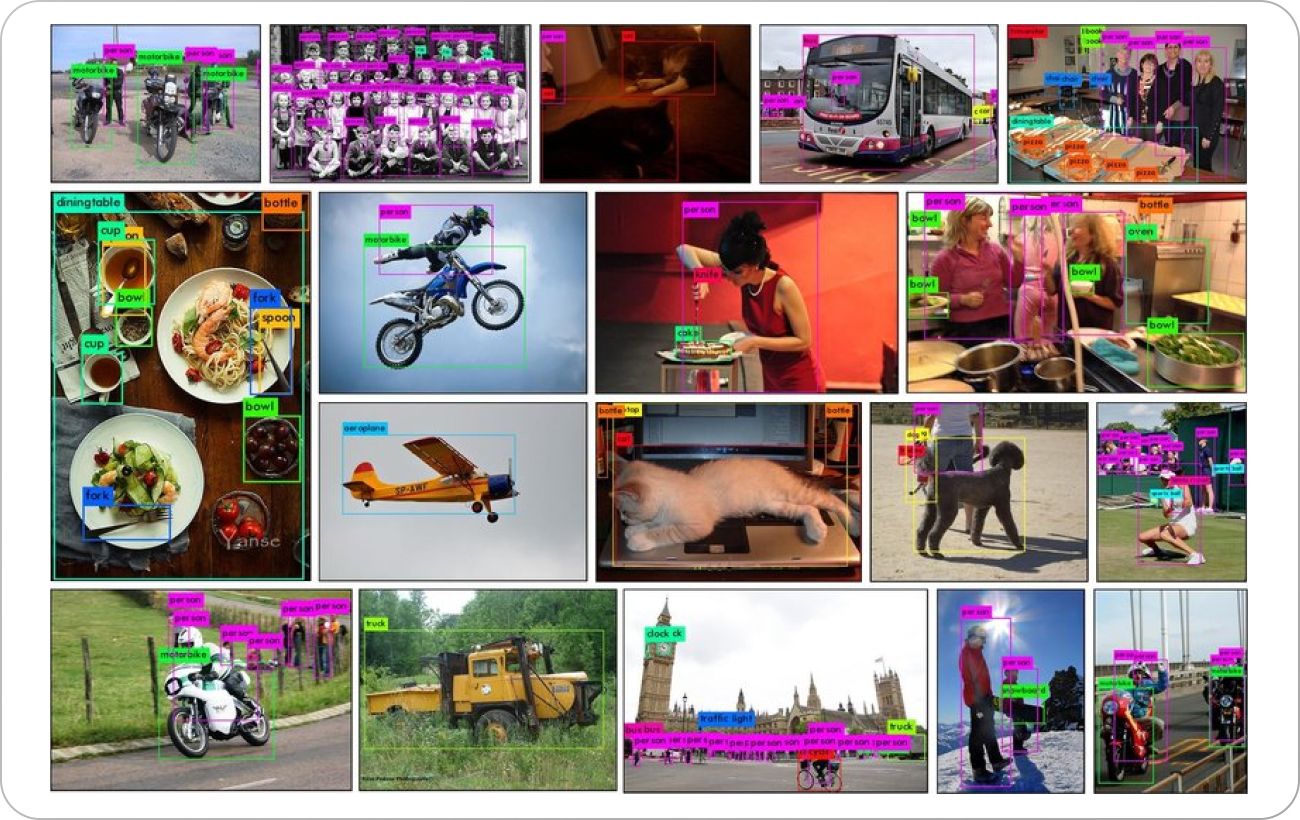
For the purposes of object detection, segmentation, and captioning, the dataset Common Objects in Context (COCO) offers labeled images.
The dataset contains over 330,000 images, featuring more than 2.5 million item instances, each meticulously labeled with bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and captions.
COCO is a versatile dataset that can be used for a wide range of computer vision tasks, including image identification, image captioning, and object tracking.
4. Cityscapes
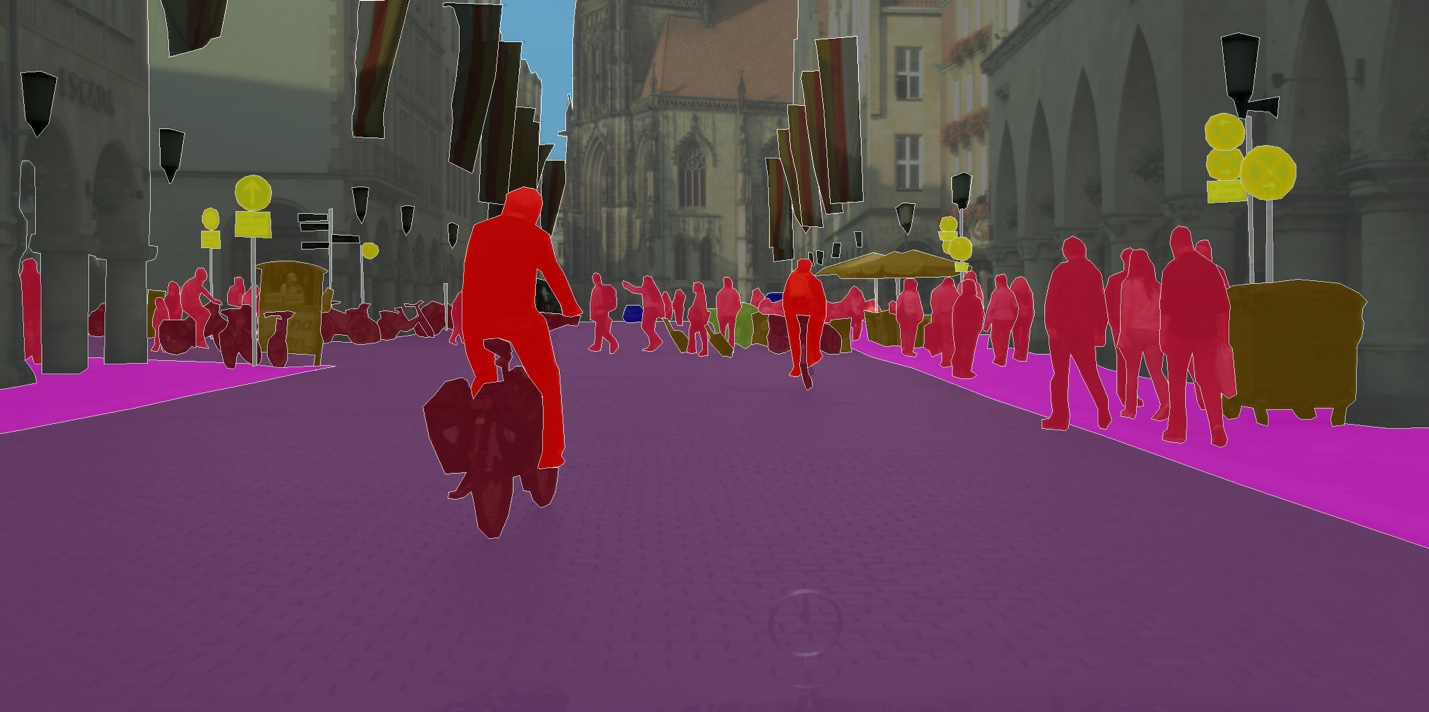

For machine learning research, the dataset Cityscapes offers labeled images of urban street scenes.
The collection includes high-resolution photographs of street scenes from 50 different cities and annotations for object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation.
Computer vision tasks involving the detection of roads, lane markings, and traffic signs can all be carried out using cityscapes.
5. ImageNet

ImageNet is a sizable collection of images and annotations that have been extensively used in object and image recognition studies.
More than 21,000 object types have been labeled with bounding boxes and segmentation masks across the dataset's more than 14 million photos.
For a variety of computer vision tasks, such as object detection, image categorization, and scene comprehension, ImageNet can be employed.
6. Open Images

Over 9 million photos with object detection annotations make up the dataset known as Open Image.
Numerous object categories, including humans, animals, automobiles, and home items, are represented in the dataset.
Various computer vision tasks, including object detection, image segmentation, and classification, can be accomplished with Open Images.
7. Aerial Image Segmentation
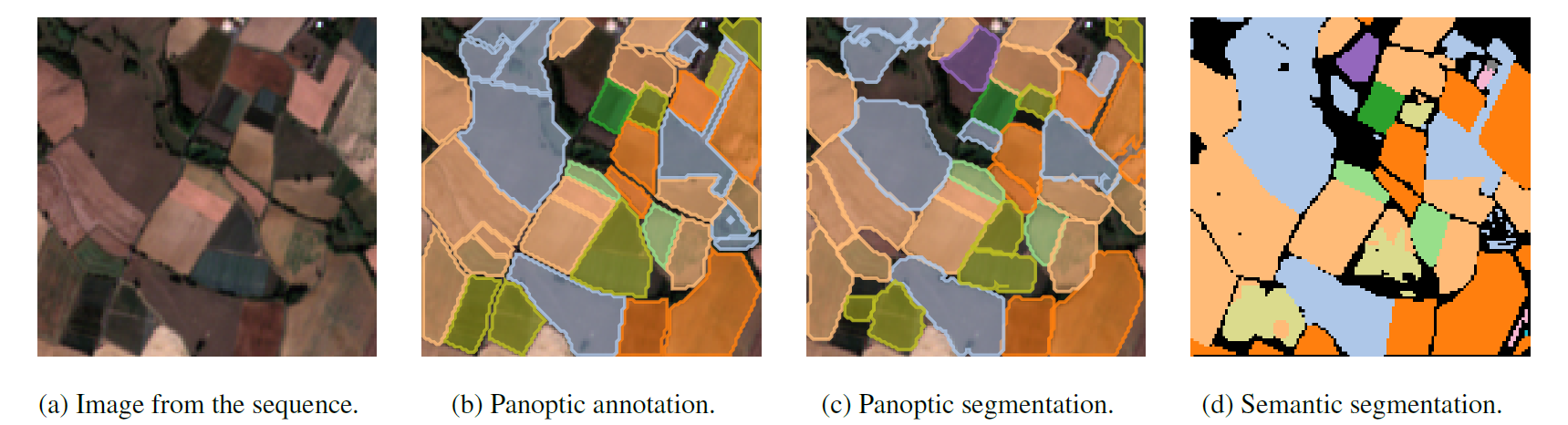

The Kaggle made the Aerial Image Segmentation dataset was made available by Kaggle for the purpose of segmenting satellite images.
The dataset consists of a number of high-resolution satellite photos of different places annotated with the locations of numerous structures, roads, and water bodies.
The dataset can be used for tasks like semantic segmentation, object detection, and classification in computer vision.
Conclusion
GeoSpatial datasets offer a multitude of data for computer vision projects, from street-level views to satellite photos.
There are many benefits of using geospatial datasets like they can provide necessary details within an image by identifying the objects present in the image and also understand the spatial context and relationships of the geographical area, leading to more accurate analysis.
These datasets offer a solid basis for creating and refining computer vision models that may glean insightful information from geographical data, making a positive impact on a variety of industries including urban planning, agriculture, and emergency response.
Labellerr's data annotation solutions ensure datasets accuracy. Streamline data preparation, improve model performance, and accelerate project timelines. Start a free trial now.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Google Earth and Google Street View?
Google Earth delivers satellite images and aerial photography of the Earth's surface, whereas Google Street View gives panoramic 360-degree street-level footage.
2. What is OpenStreetMap?
OpenStreetMap is a free and open-source mapping platform that features user-contributed map data such as roads, buildings, and landmarks.
3. What is DigitalGlobe?
DigitalGlobe is a for-profit company that sells high-resolution satellite images and geospatial content.
4. What is SpaceNet?
SpaceNet is a business, government, and charity initiative that aims to accelerate geospatial AI innovation by delivering high-quality, publically available satellite imagery datasets.
5. What are Microsoft Building Footprints?
Microsoft Building Footprints is an aerial photography file that gives exact footprints and outlines of structures.
6. Which NOAA datasets are utilized in computer vision projects?
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) supplies a variety of datasets for computer vision applications, including meteorological data, oceanographic data, and environmental imaging.

Simplify Your Data Annotation Workflow With Proven Strategies
.png)


