The Role of AI in Power Line Inspections

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Traditional Methods of Power Line Inspections
- Role of AI
- AI Solutions
- Challenges and Considerations
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Power lines are cables that carry electricity from power plants to homes, businesses, and other places where it's needed.
They're like highways for electricity, stretching across cities and countryside to deliver power to people's homes and devices.
Power line inspection is the process of checking these cables to make sure they're working safely and efficiently.
It involves looking for any problems or damage that could cause power outages or safety hazards. Inspectors use various methods, like visual inspections, flying drones equipped with cameras, or special equipment that detects issues in the lines.

The electrical grid is like a giant network that connects power plants to consumers, transmitting electricity across vast distances.
Without a reliable grid, there would be frequent power outages, disrupting daily life and potentially causing harm. Imagine not being able to turn on lights, charge phones, or run essential appliances like refrigerators or heating systems.
Reliable grids also support economic growth by providing businesses with the power they need to operate machinery and equipment.
Additionally, in emergencies or natural disasters, a reliable grid is crucial for powering emergency services and maintaining communication networks.
Overall, reliable electrical grids are the backbone of modern society, providing essential services and powering our daily lives.
Traditional Methods of Power Line Inspections
Manual Visual Inspections
Manual visual inspections involve trained personnel physically inspecting power lines and associated equipment on foot or in vehicles. They may use binoculars or telescopes for closer inspection.
They can be hazardous for inspectors, especially in remote or difficult-to-access areas. Additionally, manual inspections may overlook subtle defects or require repeated visits for comprehensive coverage.

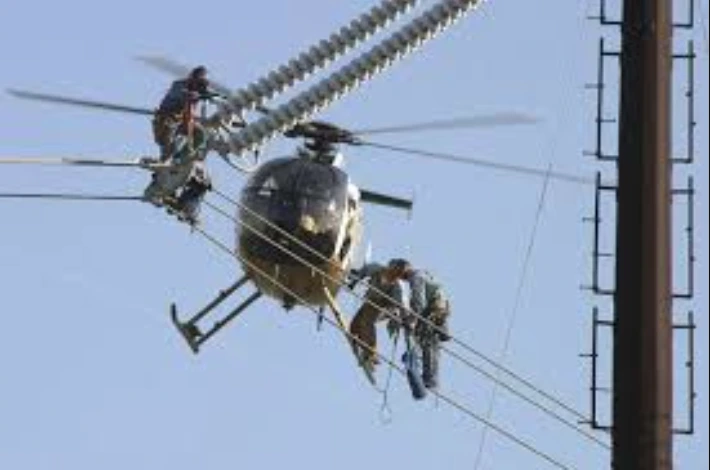
Aerial Inspections with Helicopters
Helicopters fly at low altitudes, allowing inspectors to visually inspect power lines and capture high-resolution images or videos.
Sensors may detect anomalies such as hotspots or loose connections. Aerial inspections are costly and require skilled pilots. Weather conditions can impact flight safety and data quality.
Limited field of view may result in incomplete coverage, and images may be obscured by vegetation or obstacles.

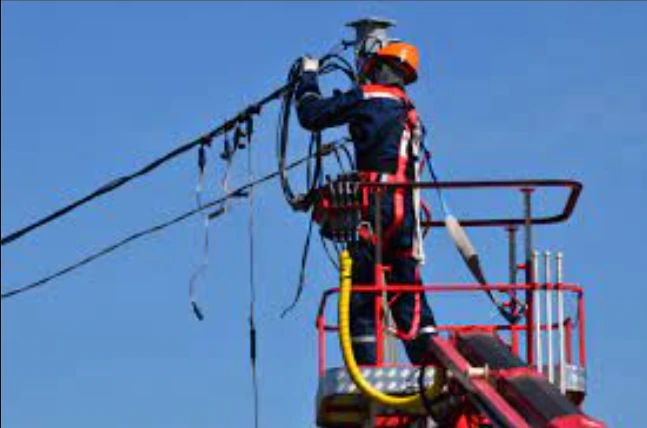
Ground-Based Inspections
Inspectors use vehicles equipped with cameras or LiDAR sensors to survey power lines from roads or access points.
They may also deploy handheld devices or climb towers for closer inspections.
Ground-based inspections may be limited by terrain or accessibility constraints. They require coordination with landowners and may disrupt traffic or local communities.
Data collection may be less comprehensive compared to aerial methods, and ground-level obstacles can obstruct views.

Role of AI
By leveraging artificial intelligence, energy utilities can transform their approach to inspecting and maintaining infrastructure.
AI-powered inspections automate repetitive tasks like data collection and analysis, enabling utilities to cover larger areas efficiently. With AI algorithms, vast amounts of data can be analyzed with precision, detecting subtle anomalies or defects that human inspectors might miss.
This results in more accurate assessments of power line condition and early identification of potential issues.
Moreover, AI-powered inspections eliminate the need for personnel to undertake hazardous tasks like climbing towers or navigating rough terrain, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and injuries for utility workers and the public.

AI solutions
Drone-Based Inspections
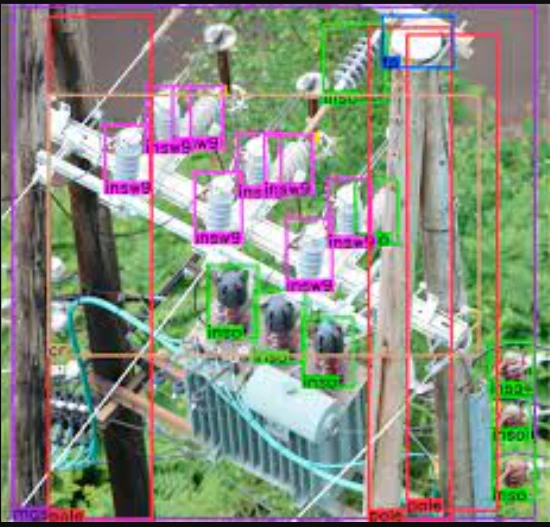
Drones fly along power line routes, capturing high-resolution images and videos. AI algorithms analyze the data to detect defects and anomalies.
Drones offer flexibility and accessibility but require skilled operators.
Drones provide rapid data collection and comprehensive coverage but require careful planning and coordination. They offer a cost-effective solution for large-scale inspections but may lack the precision of ground-based methods.

Automated Image Analysis
Automated image analysis further enhances inspection processes, leveraging AI algorithms for image recognition and anomaly detection.
This accelerates inspection workflows and improves accuracy, but may require significant computational resources.

Detection of Defects and Anomalies
Detection algorithms play a critical role in identifying defects and anomalies in power line infrastructure, enhancing inspection efficiency and accuracy.
These algorithms leverage machine learning techniques trained on labeled datasets of power line defects, enabling utilities to proactively address maintenance needs.
Similarly, vegetation identification algorithms help utilities identify encroachments near power lines, reducing the risk of outages.
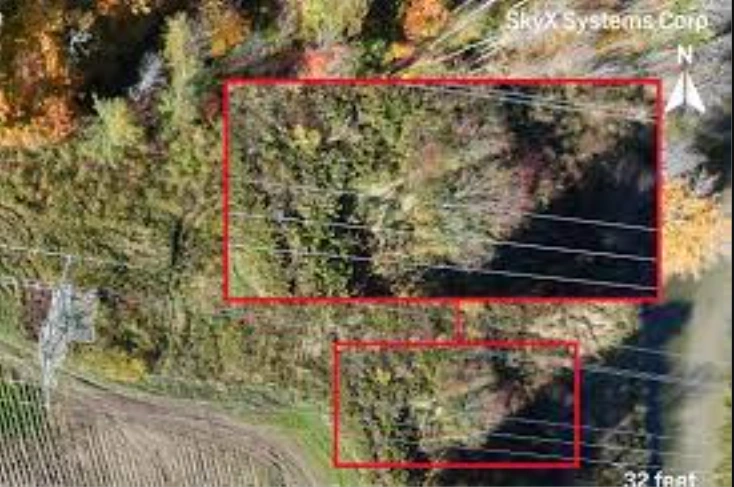

Predictive Maintenance Strategies
Predictive maintenance strategies optimize asset reliability by analyzing historical inspection data and asset performance metrics to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
These strategies offer cost savings and operational efficiencies but may require accurate data and model calibration.
Optimal Maintenance Scheduling
Optimal maintenance scheduling strategies utilize optimization algorithms to schedule maintenance activities based on asset condition and risk assessment, maximizing asset lifespan and reliability.
These strategies offer a proactive approach to maintenance planning but require accurate data and model validation to ensure effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations
Several challenges and considerations must be addressed to ensure successful deployment and operation.
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, particularly when handling sensitive information such as inspection data and infrastructure details.
Utilities must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard against unauthorized access or breaches.
Integration with existing systems poses another challenge, as AI-powered solutions need to seamlessly integrate with legacy infrastructure and workflows.
Compatibility issues and data interoperability must be addressed to ensure smooth integration and operation.
Skills and training requirements are also significant considerations, as the successful implementation of AI-powered solutions relies on skilled personnel capable of operating and maintaining these systems.
Utilities must invest in training programs to up-skill their workforce and ensure proficiency in AI technologies and methodologies.
Addressing these challenges and considerations is crucial to the successful adoption and deployment of AI-powered solutions for power line inspections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the adoption of AI in power line inspections represents a significant advancement in utility operations, offering numerous benefits in efficiency, accuracy, cost savings, and safety.
AI-powered solutions will continue to evolve, leveraging advancements in machine learning, sensor technologies, and data analytics to further enhance inspection processes and optimize maintenance strategies.
As utilities embrace these innovations, they will gain greater visibility into their infrastructure, enabling more informed decision-making and resource allocation.
Furthermore, the integration of AI with emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and 5G connectivity will enable real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, ushering in a new era of smart grid management.
By embracing these technologies and adapting to changing industry dynamics, utilities can position themselves for success in the evolving energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you inspect power lines?
Power lines are inspected using various methods, including visual inspections conducted by trained personnel, aerial inspections using helicopters or drones, and ground-based inspections using specialized equipment.
Visual inspections involve visually inspecting power line components for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion, while aerial and ground-based inspections utilize advanced technologies such as drones, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and infrared imaging to assess the condition of power lines and detect potential issues.
What is the use of drone in power line inspection?
Drones are increasingly used in power line inspection due to their ability to capture high-resolution images and videos of power line infrastructure from various angles and distances.
They can safely and efficiently inspect power lines, towers, and other components, providing valuable data for asset management, maintenance planning, and defect detection.
Drones offer several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, accessibility to hard-to-reach areas, and reduced risk to personnel compared to traditional inspection methods.
What is transmission line inspection?
Transmission line inspection involves assessing the condition and integrity of high-voltage transmission lines that carry electricity over long distances from power plants to substations or distribution networks.
Transmission line inspections aim to identify potential faults, defects, or damage that could compromise the safety, reliability, or efficiency of the electrical grid.
Transmission line inspections are critical for ensuring the reliable operation of the electrical grid and preventing power outages or equipment failures.

Simplify Your Data Annotation Workflow With Proven Strategies
.png)


