How AI-ML paved the way for self driving cars

Table of Contents
Introduction
The future is here: self-driving cars. But what's the big deal?
We're going to tell you why it's not just a big deal. It's a giant leap forward in technology and transportation, one that will change the way we live and work. But first, let's look at how AI-ML made it possible for us to have this conversation about self-driving cars today.
A vehicle that employs a network of sensors, cameras, radar, & artificial intelligence (AI) to move between locations without a human driver is referred to as a self-driving car (also known as an automated car or driver-less car). A vehicle needs to be capable of navigating to a predefined location across unsuitable roads in order to be considered completely autonomous. Self-driving cars are expected to save more than 1.3 million lives by 2050, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Artificial intelligence is the new frontier for automotive companies. From self-driving cars, to in-car infotainment and data analysis, AI is helping automakers explore new ways to make driving safer and more efficient.
The technology is already being used in a range of new ways by automakers around the world, from Tesla’s Autopilot to Daimler’s digital assistant, Mercedez-Benz’s EQR4 autonomous driving system and Audi’s R10 e-tron SUV.
The idea of self-driving cars is not new. The first such vehicles were built in the 60s and 70s. But they would only seem like a cardboard box when compared with today's technology.
Today, there are many companies developing autonomous vehicles and their technologies based on different automation level. Many of them use artificial intelligence (AI) to make their vehicles better than human drivers at driving in complex traffic situations. AI algorithms can help cars recognize objects on the road, predict what might happen next, and even react quickly to unexpected situations.
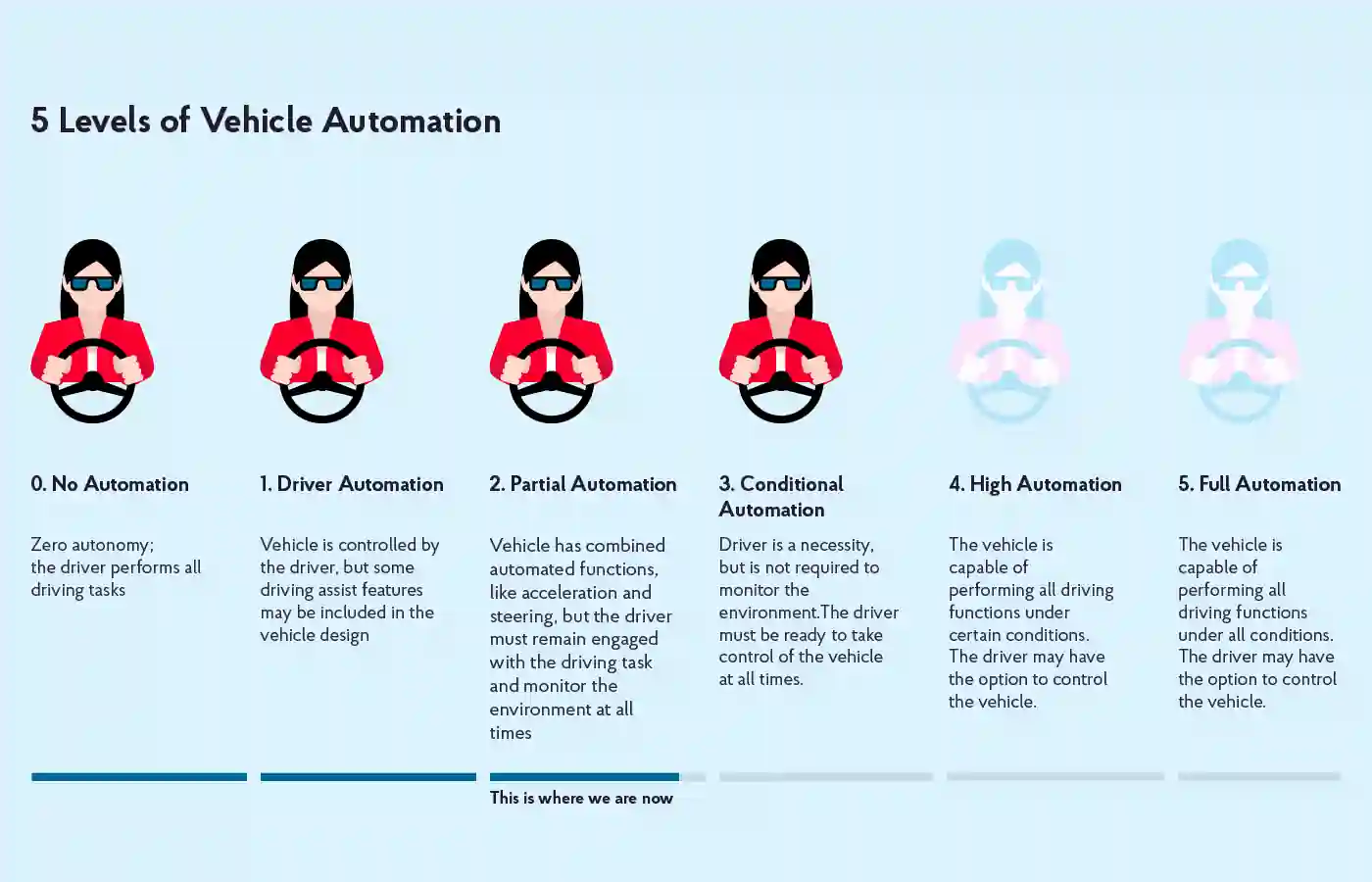
AI techniques have been applied to problems in numerous areas including computer vision, speech recognition, and machine learning. In recent years, AI has been used for tasks as diverse as spam filtering, image and video classification, language translation, and autonomous driving.
An AI-based system is usually evaluated by measuring its performance against a standard baseline model. The term "artificial intelligence" was first coined by John McCarthy at Stanford University in 1956. He also coined the term "artificial neural network".
He was trying to find a way to make computers show intelligent behavior more than humans do, but he could not find a way to do it because there was no computer that could calculate what humans are calculating on their own. This is a very simple explanation of how AI works.
The Auto Industry is going through a revolution. The automotive industry has been experiencing rapid change in recent years, which is due to many factors. One of the reasons for this is that there are many new technologies that are being developed and implemented in cars. One of these technologies is Machine Learning which is used to improve the quality of vehicles by identifying patterns in data sets.
Machine Learning can be used to identify patterns in data sets and make predictions about specific situations or conditions. This can be used to predict when a crash is likely to occur or when an airbag should be deployed based on how people drive. Machine Learning can also be used for error detection and correction, for example, if it detects that your car has skidded out of control then it will try to correct its course before it crashes into something else.
How does self-driving work?
In a world where self-driving cars are becoming more and more common, it's important to know what exactly is happening behind the scenes. Machine learning is a fundamental part of this process.
How does machine learning work?
It's actually quite simple. The brain of a human being is made up of billions of neurons (nerve cells) connected to each other with synapses. Each neuron sends out a signal at a certain frequency, which causes another neuron to fire when the signal reaches it. This creates a chain reaction that spreads through the brain like wildfire.
When you think about it, this is basically how machine learning works too. We use algorithms that connect data points together and allow them to generate new insights by making predictions based on our past experiences or current context.
In order to run the software, autonomous automobiles need sensors, actuators, sophisticated algorithms, and machine learning algorithms.
Based on a number of sensors positioned throughout the vehicle, autonomous automobiles build and update a mapping of their surroundings. Radar sensors keep track of the whereabouts of adjacent automobiles. Traffic lights, road signs, other vehicles, and pedestrians are all detected by video cameras. Lidar (light detection and ranging) sensor estimate distances, find road boundaries and recognize lane markers by reflecting light pulses off the environment around the car. When parking, ultrasonic sensors in the tires pick up on curbs and other cars.
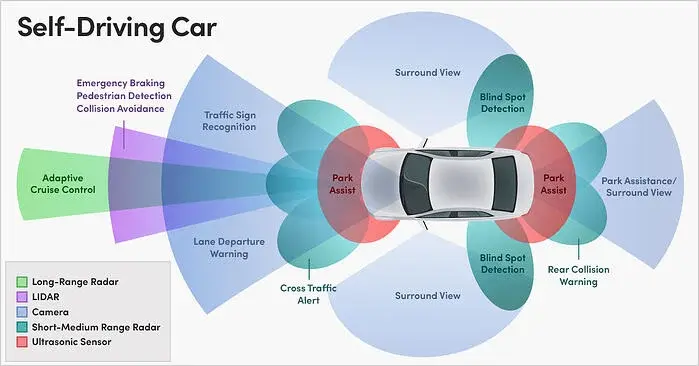
Then, sophisticated software analyses all of this sensory data, draw a path, and issues command to the actuators in the car that manages acceleration, deceleration, and steering. The software aids in adhering to traffic regulations and avoiding obstructions through the use of tough rules, obstacle detection algorithms, predictive modeling, and object identification.
Computer Vision in self-driving cars
Systems for self-driving cars are powered by AI. To create systems that can drive independently, self-driving car developers combine huge amounts of information from image recognition technologies with neural networks and machine learning.
The algorithms for machine learning are given the patterns that the neural networks found in the data. Images captured by self-driving car cameras are among the data sources used by the neural network to train itself to recognize objects such as traffic signals, trees, sidewalks, pedestrians, street signs, and other elements of a given driving environment.
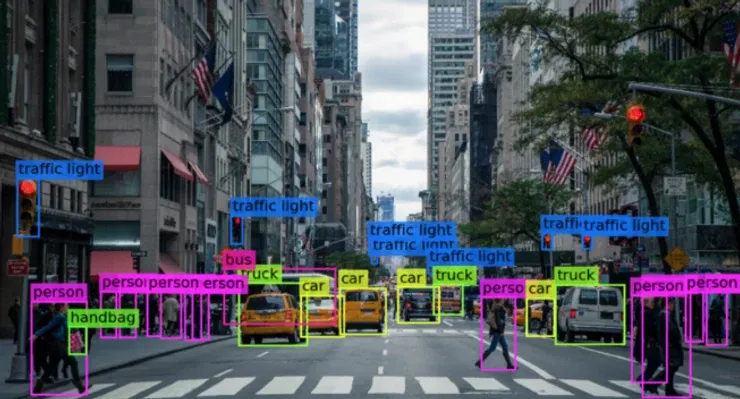
Example- Google's Waymo self-driving car project employs a combination of sensors, cameras, and lidar (light detection and ranging, a technology related to RADAR) to recognize everything that surrounds the vehicle and forecast what those items may do next. This takes place in brief intervals of time. It's crucial for these systems to be mature. The system can use deeper learning algorithms to make more sophisticated driving decisions as it accumulates more driving data.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that the future of self-driving cars is here and it's an AI-powered one. Although progress has been made toward completely autonomous vehicles, there is still a long way to go in terms of technology and adoption before driverless vehicles become the norm. In the following ten years, more autonomous vehicles should be visible on public highways. However, there is still a lot of work ahead before this can become a reality. With the improvement in levels of technology, Self-driving cars will pave their way into the roads.
If you are interested in getting more related information, then stay tuned!

Simplify Your Data Annotation Workflow With Proven Strategies
.png)


