5 Best Geospatial Image Annotation & Labeling Tools In 2025
In 2025, top geospatial image annotation tools include Labellerr, Labelbox, VGG Image Annotator (VIA), CVAT, and Kili Technology. These platforms offer precise annotations, supporting formats like GeoTIFF, JPEG2000, and more, while ensuring scalability.

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Labellerr
- Labelbox
- VGG Image Annotator (VIA)
- CVAT (Computer Vision Annotation Tool)
- Kili Technology
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Imagine you have a map that can help you spot exciting places, find hidden treasures, and understand the secrets of our Earth.
Well, guess what? That's what geospatial annotation is all about!
Geospatial annotation is adding labels to pictures or maps to tell us more about the amazing things we see from way up high in the sky.
Did you know that there are geospatial annotation tools used to annotate these maps and pictures?
These tools have labeled millions of maps and pictures accurately.
They've helped Fortune companies, researchers, and even students to understand our Earth better.
These tools are not just precise but also super fast! They've annotated large datasets efficiently, making them perfect for big projects.
And guess what? They can work with maps at different levels of detail – from high up in space to zooming in on specific places on Earth.
Now, let's explore the list of the top available Geospatial Image Annotation Tools in this blog.
Top 5 Geospatial Image Annotation Tools
1. Labellerr

Labellerr stands out as an exceptional geospatial data annotation tool, highly regarded for its accuracy and efficiency in managing detailed geospatial tasks.
Its user-friendly interface and robust functionalities make it a preferred choice among professionals in the field.
It excels in precisely annotating geospatial data, serving the diverse needs of Fortune companies, researchers, and students alike.
The tool's capability is evident in the annotated samples of geospatial data, specifically using polygon annotation.
The image below showcases Labellerr's remarkable attention to detail and meticulousness, highlighting its capability to handle complex geospatial data annotation tasks with precision.
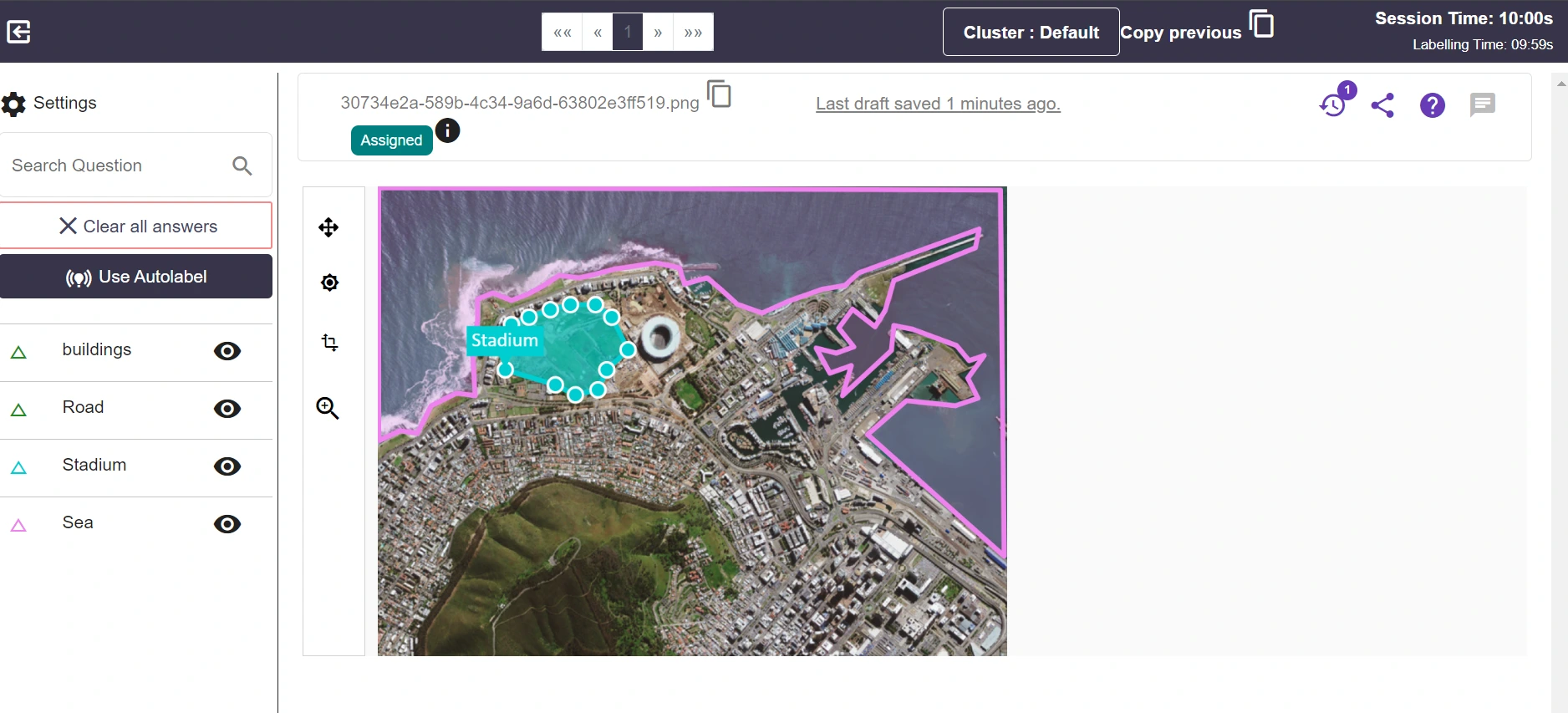
Key Features:
1. Precision Annotation
Labellerr is known for its exceptional precision in annotating geospatial data, ensuring accurate and detailed annotations for complex tasks.
2. User-Friendly Interface
The tool has an intuitive interface, making it accessible for professionals, researchers, and students with varying levels of expertise in geospatial data annotation.
3. Versatility in Format Support
It supports a wide range of geospatial image formats, including JPEG/JPG, PNG, GeoTIFF, ECW, JPEG2000, SID, NITF, and TIFF, providing flexibility and adaptability to diverse data types.
4. Efficient Polygon Annotation
Labellerr excels in polygon annotation, enabling users to precisely outline and annotate specific areas of interest within geospatial data.
5. Scalability
The tool is designed to handle large geospatial datasets efficiently, making it suitable for projects of varying sizes and complexities.
6. Multi-Resolution Support
It accommodates multi-resolution images, allowing users to work with datasets at different levels of detail seamlessly.
What makes Labellerr truly versatile is its capacity to annotate various geospatial image formats, ensuring compatibility and support for different types of geospatial data.
This includes, but is not limited to:
JPEG/JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Widely used for visual images, but may not be optimal for GIS applications due to potential image quality loss from its compression.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics): A popular raster format supporting lossless data compression, often used for web graphics.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): A versatile and widely used image format known for flexibility and compatibility with various data types, making it a popular choice in geospatial applications.
GeoTIFF: An extension of TIFF that incorporates georeferencing information, allowing correct positioning on the Earth's surface.
ECW (Enhanced Compression Wavelet): Known for highly efficient compression methods while maintaining good image quality, making it suitable for storing large geospatial datasets.
JPEG2000: An improvement over traditional JPEG, providing better compression with minimal loss of image quality and supporting both lossless and lossy compression.
NITF (National Imagery Transmission Format): Primarily used in military and intelligence applications, serving as a standard format for storing and transmitting imagery along with associated metadata.
SID (MrSID - Multi-resolution Seamless Image Database): Utilizes wavelet compression, ideal for compressing large images and enabling easy browsing at different resolutions.
Pros:
-> High Accuracy
-> Wide Format Compatibility
-> Efficient Compression Methods
-> Scalability
-> Ease of Use
Cons:
-> Price Consideration for individual users or small scale projects
2. Labelbox

Labelbox is a versatile platform that supports geospatial image annotation. It allows users to annotate images with bounding boxes, polygons, and key points.
This Annotation Tool is very precise for images of maps and locations.
Imagine you have a map, and you want to make it even better by adding special details to it. That's exactly what this tool does for all kinds of maps and pictures with important information.
Key Features:
1. Make Maps More Useful
Labelbox helps make maps more informative by adding labels directly on them.
It's like when you draw on a map to show where the treasure is, but Labelbox does it in a high-tech way!
2. Label Faster with Help
Labeling means adding details to the map. With Labelbox, you can do it faster with a little help from foundation models.
These models do some work first, and then you can correct and improve it. This way, it's like teamwork between humans and computers!
3. Collaboration
The platform allows multiple users to collaborate seamlessly, facilitating teamwork in large-scale annotation projects.
4. Integration
Labelbox integrates well with popular machine learning frameworks, enabling a smooth transition from annotation to model training.
5. The Super Map Tool
It can do many things like drawing boxes, lines, and even showing different layers of information.
It's not just powerful but also easy to use, making it a good choice for geospatial annotation.
6. Bring in the Experts
If you ever need some extra help, Labelbox can connect you with the best experts.
They are good at adding labels to maps and can do it quickly.
7. Fixing Mistakes Made Easy
If you make a mistake while annotating, Labelbox makes it super easy to find and fix errors.
Use Cases:
Labelbox is widely used in various industries, such as agriculture (crop monitoring), urban planning (building detection), and environmental monitoring (land cover classification).
Pros:
-> Intuitive user interface
-> Versatile annotation capabilities
-> Robust collaboration features
-> Integration with machine learning workflows
Cons:
-> Pricing might be a consideration for small-scale projects
3. VGG Image Annotator (VIA)

VIA, developed by the Visual Geometry Group at the University of Oxford, is an open-source geospatial image annotation tool.
It's a web-based platform that provides flexibility and customization for annotating various image types.
Key Features:
1. Annotation Flexibility
VIA allows users to annotate geospatial images with bounding boxes, polygons, points, and lines, supporting a broad spectrum of annotation tasks.
2. Open Source
Being open source, VIA offers transparency and flexibility, allowing users to modify the tool to suit their specific needs.
3. Platform Independence
VIA is accessible through a web browser, making it platform-independent and easy to deploy.
Use Cases:
VIA is particularly suitable for researchers and developers who need a customizable annotation tool for diverse geospatial image analysis projects.
Pros:
-> Open-source and customizable
-> Supports multiple annotation types
-> Web-based, platform-independent
Cons:
-> Steeper learning curve for users unfamiliar with open-source tools
4. CVAT (Computer Vision Annotation Tool)

CVAT is a powerful, open-source annotation tool developed by Intel.
It supports geospatial image annotation and various computer vision tasks, making it a valuable resource for both researchers and industry professionals.
Key Features:
(i) Scalability
CVAT is designed to handle large-scale annotation projects, making it suitable for geospatial datasets with numerous images.
(ii) Collaboration
The tool provides collaborative annotation capabilities, allowing multiple annotators to work on the same project simultaneously.
(iii) Multiple Annotation Types
CVAT supports multiple annotation types, such as bounding boxes, polygons, and key points, ensuring versatility in geospatial data annotation.
Use Cases:
CVAT is widely employed in projects involving satellite and aerial imagery annotation, land cover classification, and object detection in geospatial datasets.
Pros:
-> Scalable for large projects
-> Collaboration features
-> Supports multiple annotation types
Cons:
-> May require some setup and configuration
5. Kili Technology

Kili Technology is a comprehensive data annotation platform that goes beyond geospatial image annotation, supporting a wide range of data types.
It is designed to provide end-to-end solutions for creating labeled datasets efficiently.
Key Features:
1. Annotation Variety
Kili supports various annotation tasks, including geospatial image annotation, text annotation, and more.
This diversity makes it suitable for projects that require annotations across different modalities.
2. Active Learning
Kili incorporates active learning capabilities, allowing the platform to learn from human annotations and improve its performance over time.
This feature contributes to increased efficiency in the annotation process.
3. Data Management
The platform offers advanced data management tools, including versioning and collaboration features.
This ensures efficient organization and tracking of datasets, particularly in large-scale projects.
Use Cases:
Kili Technology is an ideal choice for projects with complex annotation requirements across different data types.
Its active learning capabilities make it particularly efficient for tasks where continuous improvement is crucial.
Pros:
-> Diverse annotation capabilities
-> Active learning for improved efficiency
-> Advanced data management features
Cons:
-> May have a steeper learning curve for new users due to its comprehensive feature set
Conclusion
Choosing the right geospatial image annotation tool is crucial for accurate and efficient data labeling.
Labellerr stands out with its precision annotation, user-friendly interface, and versatility in supporting various geospatial formats. Labelbox offers a collaborative platform with helpful features like foundation models, making it powerful and user-friendly.
VGG Image Annotator (VIA) provides flexibility and customization for researchers and developers, while CVAT, an open-source tool, is scalable and suitable for large-scale projects.
Kili Technology offers a comprehensive solution with diverse annotation capabilities and active learning features, making it efficient for complex tasks.
Each tool has its pros and cons, and the choice depends on specific project requirements. Overall, these tools play a vital role in enhancing the accuracy and usability of geospatial data across various industries.
Read our other listicles:
1. 7 Best Text Annotation & Labeling Tools In 2025
2. 6 Best Image Recognition Tools in 2025
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the challenges in geospatial image annotation tools?
Geospatial image annotation tools face several challenges. One major issue is the complexity of interpreting diverse geographical features, such as terrain, buildings, and vegetation, which requires sophisticated algorithms for accurate labeling.
Additionally, the sheer volume of geospatial data poses a challenge in terms of scalability and efficiency. Another obstacle is ensuring the consistency and quality of annotations across different annotators and datasets, as subjective interpretations may vary.
Lastly, keeping up with rapid advancements in satellite and aerial imagery technology requires continuous tool adaptation to handle diverse and evolving data sources effectively.
2. What is geosatellite image annotation?
Geosatellite image annotation involves adding labels or markings to satellite images to identify and describe specific features on the Earth's surface.
This process helps in training computer algorithms to recognize and understand different elements like buildings, roads, and vegetation in the images.
Annotations play a crucial role in applications like mapping, environmental monitoring, and disaster response, enabling computers to analyze and interpret geospatial data accurately.
3. Where can I find geospatial data and imagery?
Geospatial data and imagery can be found from various sources, including government agencies, research institutions, and commercial providers.
Many government agencies, such as the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the European Space Agency (ESA), offer free access to geospatial data.
Online platforms like Google Earth, NASA Worldview, and OpenStreetMap also provide access to interactive maps and satellite imagery.
Additionally, commercial providers like Maxar, Airbus, and Planet offer high-resolution satellite imagery for purchase.
Open data initiatives and online repositories are valuable resources for accessing geospatial datasets for research, analysis, and mapping purposes.

Simplify Your Data Annotation Workflow With Proven Strategies
.png)


